Full load motor torque 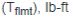 |
Horsepower (P), hp
Shaft speed (N), rpm
5252 = Constant
|
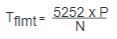 |
Average dynamic braking torque 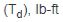 |
Total inertia reflected to brake 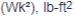 Shaft speed at brake (N), rpm
Desired stopping time (t), seconds
308 = Constant
|
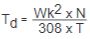 |
| Static torque (T), lb-ft |
Force (F), lb
Pulley or drum radius, (R), ft
|
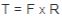 |
Overhauling dynamic torque reflected to brake shaft .JPG.aspx) |
Weight of overhauling load (W), lb
Linear velocity of descending load (V), ft/min
Shaft speed at brake (N), rpm
0.158 = Constant
|
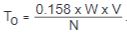 |
Static torque of brake 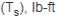 |
Dynamic braking torque required 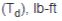 0.8 = Constant (derating factor)
|
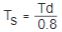 |
|
Inertia of rotating load reflected to
brake shaft .JPG.aspx) |
Inertia of rotating load .JPG.aspx) Shaft speed at load 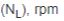 Shaft speed at brake .JPG.aspx) |
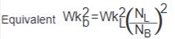 |
|
Equivalent inertia of linear moving load
reflected to brake shaft .JPG.aspx) |
Weight of linear moving load (W), lb
Linear velocity of load (V), ft/min
Shaft speed at brake .JPG.aspx) 2 = Constant
|
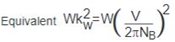 |
Kinetic energy of rotating load, 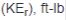 |
Inertia of rotating load reflected to brake shaft
Shaft speed at brake .JPG.aspx) 5875 = Constant
|
.JPG.aspx?width=100&height=37) |
Kinetic energy of linear moving load .JPG.aspx) |
Weight of load (W), lb
Linear velocity of load (v), ft/sec
g = Gravitational acceleration constant 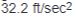 |
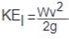 |
| Change in potential energy (PE), ft-lb |
Weight of overhauling load (W), lb
Distance load travels (s), ft
|
PE = Ws |
Total energy absorbed by brake 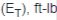 |
Total linear kinetic energy 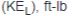 Total rotary kinetic energy 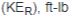 Potential energy converted to kinetic energy
(PE), ft-lb
|
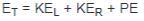 |
|
Thermal capacity required for rotational or linear
moving loads (TC), hp-sec/min
|
Total system inertia reflected to brake shaft
Shaft speed at brake 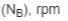 Number of stops per minute (n), not less
than one 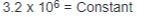 |
.JPG.aspx?width=110&height=41) |
|
Thermal capacity required for overhauling loads
(TC), hp-sec/min
|
Total energy brake absorbs .JPG.aspx) Number of stops per minute (n), not less
than one 550 = Constant
|
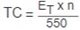 |
| Linear velocity, ft/min |
N = rpm
Diameter (D), ft
|
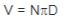 |